In this article we are going to see how Drupal serves configurations across the environments, which can be well maintained with help of some contributed modules and version control.
Drupal 8 onwards configuration has been saved in the yml files in a consistent manner, which includes all the enabled modules, all the content types, vocabularies, fields & views.
Making the configurations directly in the higher environment is not recommended, every configuration should go to a higher environment via code change (which is maintained in version control).
Drupal core provides the feature to import, export & synchronise the configurations. Drupal provides drush commands for the same feature (which is even more helpful).
$settings['config_sync_directory'] = '../config/sync';
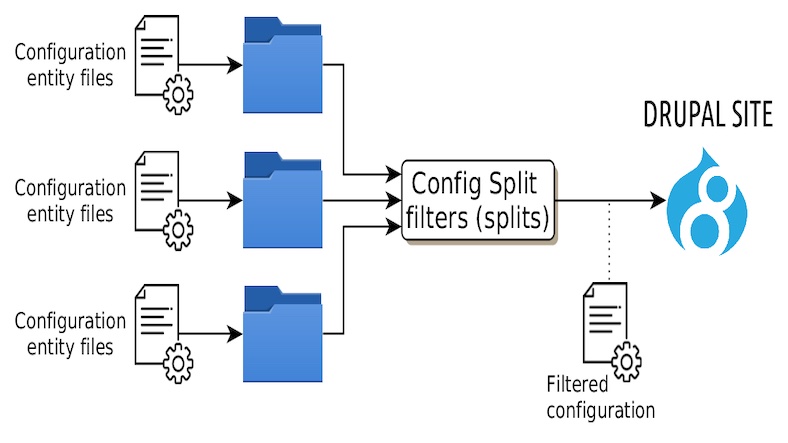
We can use the Configuration Split contributed module. This module allows us to create a group of configurations that can be exported to different folders during exporting. This can be configured from the settings.php, like what folder should be active for which environment.
Create four environments in the config split configuration.
- Local
- Dev
- Test
- Live
Here goes the folder structure of the config.
config
And in the settings.php file, configuration for this should go like below
switch ($env) {
case ‘dev’:
$config['config_split.config_split.local’]['status'] = FALSE;
$config['config_split.config_split.dev']['status'] = TRUE;
$config['config_split.config_split.test']['status'] = FALSE;
$config['config_split.config_split.live']['status'] = FALSE;
….
Similarly set for all env’s
….
case ‘default’:
$config['config_split.config_split.local’]['status'] = TRUE;
$config['config_split.config_split.dev']['status'] = FALSE;
$config['config_split.config_split.test']['status'] = FALSE;
$config['config_split.config_split.live']['status'] = FALSE;
}
To export & import the configuration, you can use the drush cex & drush cim, and commit the changes to the repository.
This way would be best to manage the configuration in the drupal applications.